IELTS READING (from 1 to 14)-listen to the reading passage

THE ROCKET – FROM EAST TO WEST
E It was not until the eighteenth century that Europe became seriously interested in the possibilities of using the rocket itself as a weapon of war and not just to propel other weapons. Prior to this, rockets were used only in pyrotechnic displays. The incentive for the more aggressive use of rockets came not from within the European continent but from far-away India, whose leaders had built up a corps of rocketeers and used rockets successfully against the British in the late eighteenth century. The Indian rockets used against the British were described by a British Captain serving in India as ‘an iron envelope about 200 millimetres long and 40 millimetres in diameter with sharp points at the top and a 3m-long bamboo guiding stick’. In the early nineteenth century, the British began to experiment with incendiary barrage rockets. The British rocket differed from the Indian version in that it was completely encased in a stout, iron cylinder, terminating in a conical head, measuring one metre in diameter and having a stick almost five metres long and constructed in such a way that it could be firmly attached to the body of the rocket. The Americans developed a rocket, complete with its own launcher, to use against the Mexicans in the mid-nineteenth century. A long cylindrical tube was propped up by two sticks and fastened to the top of the launcher, thereby allowing the rockets to be inserted and lit from the other end. However, the results were sometimes not that impressive as the behaviour of the rockets in flight was less than predictable. Since then, there have been huge developments in rocket technology, often with devastating results in the forum of war. Nevertheless, the modern day space programs owe their success to the humble beginnings of those in previous centuries who developed the foundations of the reaction principle. Who knows what it will be like in the future?
Questions 1-4
Reading passage 11 has six paragraphs labelled A-F.
Choose the most suitable headings for paragraphs B-E from the list of headings below.
Write the appropriate numbers (i-ix) in boxes 1-4 on your answer sheet.
| List of Headings
i How the reaction principle works |
Example Paragraph A Answer ii
1. Paragraph B
2. Paragraph C
3. Paragraph D
4. Paragraph E
Questions 5 and 6
Choose the appropriate letters A-D and write them in boxes 5 and 6 on your answer sheet.
5 The greatest outcome of the discovery of the reaction principle was that
A rockets could be propelled into the air.
B space travel became a reality.
C a major problem had been solved.
D bigger rockets were able to be built.
6 According to the text, the greatest progress in rocket technology was made
A from the tenth to the thirteenth centuries.
B from the seventeenth to the nineteenth centuries.
C from the early nineteenth to the late nineteenth century.
D from the late nineteenth century to the present day.
Questions 7-10
From the information in the text, indicate who FIRST invented or used the items in the list below.
Write the appropriate letters A-E in boxes 7-10 on your answer sheet.
NB You may use any letter more than once.
| Example Answer rockets for displays A |
7 black powder
8 rocket-propelled arrows for fighting
9 rockets as war weapons
10 the rocket launche
| FIRST invented or used by A the Chinese B the Indians C the British D the Arabs E the Americans |
Questions 11-14
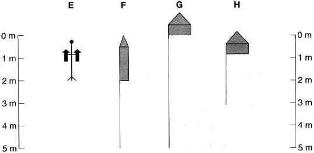
Look at the drawings of different projectiles below, A-H, and the names of types of projectiles given
in the passage, Questions 11-14. Match each name with one drawing.
Write the appropriate letters A-H in boxes 11-14 on your answer sheet.
| Example Answer The Greek ‘pigeon of Archytas’ C |
11 The Chinese ‘basket of fire’
12 The Arab ‘egg which moves and burns’
13 The Indian rocket
14 The British barrage rocket
1. iv 2. i 3. v 4. vii 5. B 6. D 7. A 8. A 9. B 10. E 11. B 12. E 13. F 14. G
